
Intrapartum amniotic fluid index: a poor diagnostic test for adverse perinatal outcome J Reprod Med 1996 41: 860–6Ĭhauhan SP, Magann EF, Perry KG, Morrison JC. Intrapartum amniotic fluid volume at term: association of ruptured membranes, oligohydramnios, and increased fetal risk J Reprod Med 1990 35: 719–23Ĭhauhan SP, Cowan BD, Magann EF et al. Amniotic fluid index and prolonged antepartum fetal heart rate decelerations Obstet Gynecol 1992 79: 558–60 Amniotic fluid volume assessment using the four-quadrant technique in the pregnancy at 36–42 weeks gestation J Reprod Med 1997 32: 540–2 Phelan JP, Smith CV, Broussard P, Small M. The four-quadrant assessment of amniotic fluid volume: an adjunct to antepartum fetal heart rate testing Obstet Gynecol 1987 70: 353–6 Rutherford SE, Phelan JP, Smith CV, Jacobs N. Longitudinal measurement of amniotic fluid index in postterm pregnancies and its association with fetal outcome Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995 172: 142–6 The role of ultrasound assessment of amniotic fluid volume in the management of the postdate pregnancy Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985 151: 304–8ĭivon MY, Marks AD, Henderson C.
Phelan JP, Platt LD, Yeh S-Y, Broussard P, Paul RH. Non-quantitative estimation of amniotic fluid volume in suspected prolonged pregnancy J Perinat Med 1980 8: 249–51 Oligohydramnios: clinical association and predictive value for intrauterine growth retardation Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983 146: 271–6Ĭrowley P. Qualitative amniotic fluid volume determination by ultrasound: antepartum detection of intrauterine growth retardation Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981 139: 254–8 Antepartum fetal evaluation: development of a fetal biophysical profile Am J Obstet Gynecol 1980 136: 787–95 Although in our population it is not predictive of adverse perinatal outcome as measured by low Apgars and NICU admissions, this may be reflective of the aggressive antepartum and intrapartum management that these patients received. ROCs produced no diagnostic cutoff values for AFI or largest pocket and prediction of any of the chosen parameters.ĬONCLUSIONS: Antepartum oligohydramnios is associated with an increased risk of fetal heart rate abnormalities. Subjects with an AFI of 5.0 cm or less had a higher rate of cesarean for fetal distress, but this did not reach statistical significance. RESULTS: An AFI of 5.0 cm or less was significantly associated with an abnormal antepartum fetal heart rate (FHR) tracing but not with cesarean delivery, meconium-stained fluid, Apgars less than 7, or NICU admission. Chi-square analysis, Fisher's exact test, t tests and receiver-operator curves (ROCs) were used for analysis. Inclusion criteria included a nonanomalous fetus and delivery within 7 days of the last antepartum surveillance test (modified biophysical profile). Data, including the reasons for testing, the testing results, and pregnancy outcome were abstracted from these records. STUDY DESIGN: The antepartum testing records of 779 women seen over a 12-month period were reviewed.

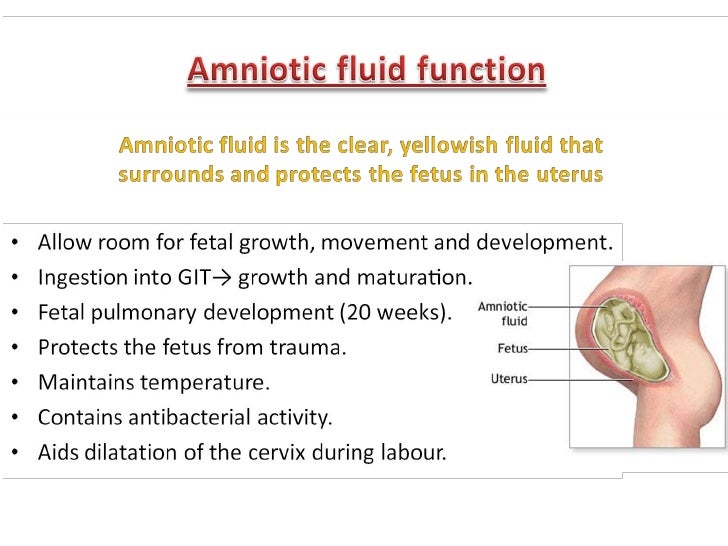
OBJECTIVE: To determine whether an antepartum amniotic fluid index (AFI) of 5.0 cm or less is a predictor of adverse perinatal outcome.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
